The Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet, originating from the countries that border the Mediterranean Sea, has long been celebrated for its numerous health benefits and is widely regarded as one of the healthiest dietary patterns available. This diet is not a single prescribed way of eating, but rather a collection of eating habits traditionally followed by the people of Southern Europe, including Italy, Greece, Spain, and parts of the Middle East.
Its recognition on a global scale escalated with growing evidence suggesting that it plays a significant role in promoting heart health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and promoting longevity. The Mediterranean Diet emphasizes the intake of whole foods, healthy fats, and moderate proteins, reflecting the traditional ways of life in these regions.
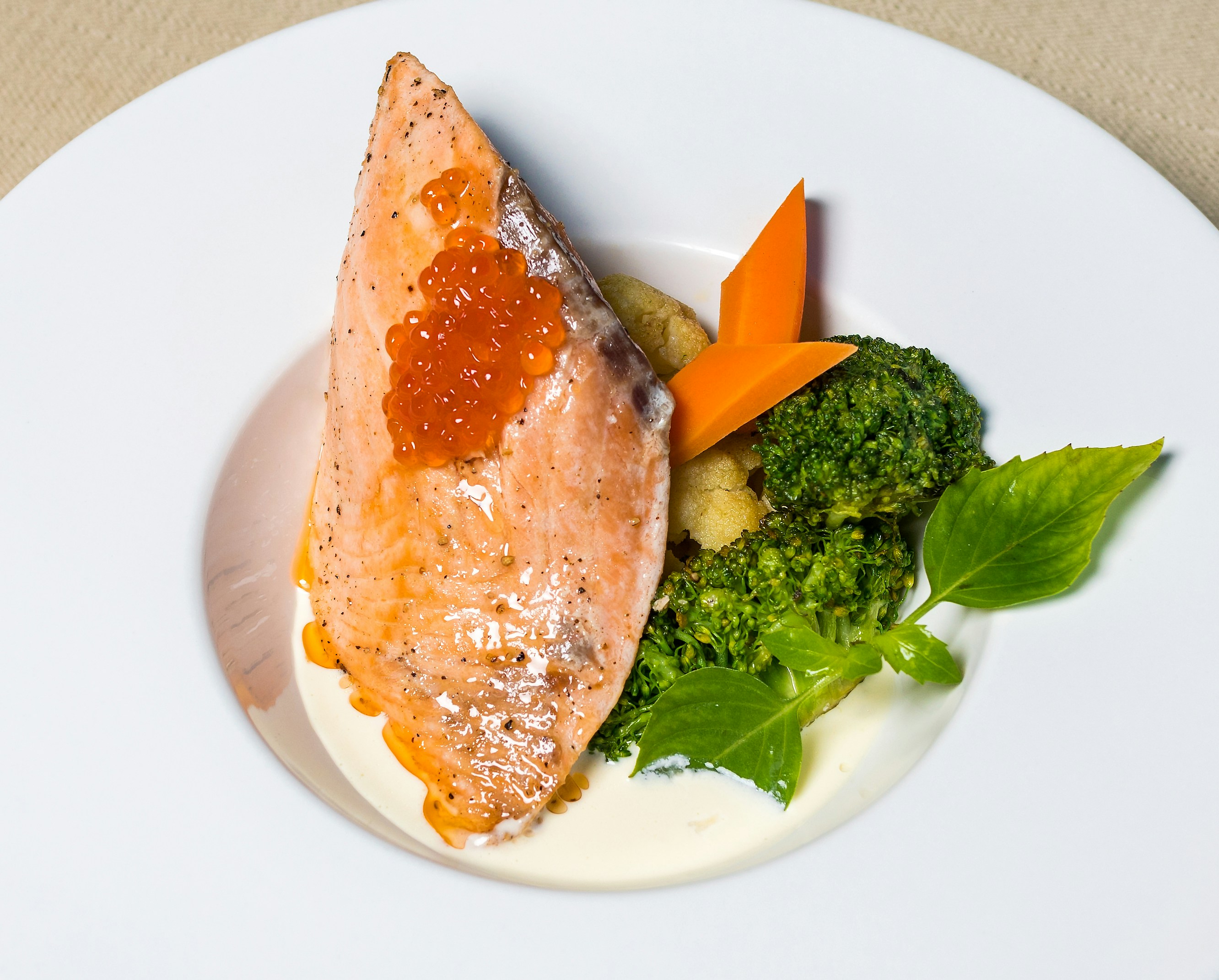
At its core, the diet prioritizes the consumption of a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes, providing a rich source of essential nutrients and dietary fiber. It also heavily features healthy fats, particularly from olive oil, which is a staple in Mediterranean cooking. Fish and seafood are preferred sources of protein, consumed at least a couple of times a week, while the intake of red meat is limited. Dairy products, particularly yogurt and cheese, are eaten in moderation, and wine is often enjoyed with meals in small quantities.
The unique aspects of the Mediterranean Diet also include the minimal use of processed foods and refined sugars, promoting a natural and unrefined approach to eating. Meals are often shared with family and friends, emphasizing the social component of dining which contributes to overall well-being.
This introduction sets the stage for a deeper exploration of the Mediterranean Diet, shedding light on its individual components and how they contribute to its overarching health benefits
Core Principles of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet is revered not only for its health benefits but also for its emphasis on using a variety of natural and wholesome ingredients. At the core of this diet are fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods form the foundation and are recommended for daily consumption due to their rich nutrient profiles and excellent sources of fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. Diverse and colorful fruits and vegetables should dominate your plate, each bringing its unique health benefits and adding flavor and texture to meals.
Olive oil stands out as the primary source of fat in the Mediterranean Diet. Extra virgin olive oil, in particular, is highly favored for its unprocessed state, ensuring that it retains all its beneficial nutrients, such as monounsaturated fats and polyphenols, known for supporting heart health. Swapping other fats, such as butter or margarine, for olive oil can lead to improved cholesterol levels and a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Fish and seafood are key players in this diet, recommended not only for their high-quality protein but also for their omega-3 fatty acids content, which promotes cardiovascular health and reduces inflammation. Aiming for at least two servings of fish per week, such as salmon, mackerel, or sardines, aligns with the dietary guidelines. Poultry and eggs are consumed in moderation and should replace red meat whenever possible, further contributing to the diet’s focus on lean protein sources.
While red meat and dairy products are not excluded, their intake is to be limited. Red meat, when consumed, should be lean and in modest amounts. Dairy is best enjoyed in the form of yogurt and cheese, often in smaller quantities. This moderation helps manage saturated fat intake and supports the heart-healthy nature of the diet.
In essence, the Mediterranean Diet’s principles revolve around prioritizing plant-based foods, choosing healthy fats, and balancing protein intake with an emphasis on fish and poultry. This holistic approach not only aids in weight management and disease prevention but also encourages a sustainable and enjoyable way of eating.
Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet is renowned for its numerous health benefits, supported by a wealth of scientific studies and research. Among the primary advantages, adherence to this diet has been significantly associated with reduced risks of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Research published in the New England Journal of Medicine indicates that individuals following a Mediterranean Diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and olive oil experience a 30% reduction in cardiovascular risks compared to those on low-fat diets.
Another pivotal benefit of the Mediterranean Diet is its efficacy in promoting weight management. The diet’s emphasis on whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats results in sustainable weight loss and maintenance. A systematic review in the International Journal of Obesity highlights that individuals on this dietary regimen often exhibit better weight control and lower BMI indexes. These findings suggest that the Mediterranean Diet could be a viable option for those seeking long-term weight management solutions.
Cognitive health is another area where the Mediterranean Diet exhibits promising benefits. Research from the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference suggests that adherence to this diet can slow cognitive decline and reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. The diet’s abundance of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties from foods like blueberries, leafy greens, and fish improve brain health and cognitive function.
In terms of longevity, studies have shown that populations adhering to Mediterranean Diet lifestyles tend to live longer, healthier lives. An analysis in the BMJ (British Medical Journal) found that adherence to this diet correlates with a 25% reduction in all-cause mortality. This is likely due to the combined effects of nutrient-rich, antioxidant-laden foods that combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
Supporting these scientific findings, personal testimonials and expert opinions further underscore the Mediterranean Diet’s health impacts. Dietitian Jane Doe highlights, “My clients adopting the Mediterranean Diet report increased energy levels, better mood, and overall improved well-being.” Such endorsements from nutrition professionals add practical insights into the diet’s daily applicability and effectiveness.
Meal Planning and Recipes
Incorporating the Mediterranean Diet into your daily routine can be a seamless transition with a bit of thoughtful meal planning and a few strategic shopping trips. The key to succeeding with this diet lies in its emphasis on fresh, whole foods, balanced meals, and flavorful, nutrient-rich recipes.
Begin your day with a Mediterranean-inspired breakfast. A simple and nutritious choice could be Greek yogurt topped with fresh berries, a drizzle of honey, and a sprinkle of nuts. This provides a good balance of protein, healthy fats, and fiber. Another breakfast option is avocado toast on whole-grain bread, garnished with cherry tomatoes and a dash of extra virgin olive oil.
For lunch, a classic Greek salad can be both satisfying and nutritious. Combine crisp cucumbers, ripe tomatoes, Kalamata olives, red onion, and feta cheese, and then dress it with olive oil and lemon juice. Pair it with a serving of whole grain pita or a small portion of grilled chicken to boost protein intake.
Dinner options on the Mediterranean Diet are both diverse and flavorful. Consider preparing a simple baked salmon dish. Marinate the salmon in olive oil, lemon juice, garlic, and fresh herbs such as dill or thyme. Bake it alongside a medley of roasted Mediterranean vegetables like zucchini, bell peppers, and eggplant. This meal is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, essential vitamins, and fiber.
Snacks can also align with Mediterranean principles. Opt for a handful of nuts, a piece of fruit, or a small serving of hummus with sliced vegetables. These snacks are not only nutritious but also keep you feeling full between meals.
To ensure you have all the ingredients you need, preparing a Mediterranean Diet-friendly shopping list is crucial. Stock up on fresh vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, seeds, lean proteins, and high-quality olive oil. Having these essentials on hand makes it easier to prepare balanced and delicious meals throughout the week.
Embracing the Mediterranean Diet can be a delicious journey toward better health. By planning your meals carefully and incorporating a variety of foods that adhere to the diet’s principles, you can enjoy flavorful dishes that support your overall well-being.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
The Mediterranean Diet has gained widespread acclaim for its health benefits, yet several myths and misconceptions persist about its components and overall feasibility. One of the most prevalent misunderstandings concerns the diet’s fat content. Contrary to popular belief, the Mediterranean Diet does not advocate for low-fat consumption. Instead, it emphasizes the intake of healthy fats, particularly from olive oil, nuts, and fish. These fats are rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which have been shown to support cardiovascular health.
Another frequent misconception revolves around the role of carbohydrates in the Mediterranean Diet. Some might incorrectly assume that the diet is low in carbohydrates. In reality, it encourages the consumption of complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables. These complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy and are an essential component of the diet, promoting a balanced nutritional intake.
The purported expense of following the Mediterranean Diet also sometimes deters individuals. While it’s true that certain ingredients like extra-virgin olive oil and fresh seafood can be costly, the diet also includes many affordable staples such as beans, lentils, whole grains, and seasonal produce. By focusing on these economical options and incorporating occasional higher-cost items, the Mediterranean Diet can be accessible on a budget.
Additionally, some people mistakenly believe that the Mediterranean Diet is solely about the foods consumed. While nutrition is a significant part, the diet also encompasses lifestyle choices such as regular physical activity, mindful eating, and social interactions during meals. These elements collectively contribute to the overall health benefits associated with the Mediterranean lifestyle.
By clarifying these common myths and misconceptions, individuals can better appreciate the holistic approach of the Mediterranean Diet and make informed decisions about incorporating its principles into their daily routines.
Getting Started with the Mediterranean Diet
Embarking on the journey of adopting the Mediterranean Diet can be both exciting and rewarding. To ensure a seamless transition, it is vital to set realistic goals and make small, sustainable changes. This approach will help you acclimate to the new dietary habits without feeling overwhelmed. Begin by gradually incorporating more vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and healthy fats into your meals. These components are the cornerstones of the Mediterranean Diet and form the foundation of its numerous health benefits.
One practical way to start is by reshaping your breakfast routine. Consider replacing sugary cereals with oatmeal topped with fresh fruits and nuts, or enjoy Greek yogurt with a drizzle of honey and a handful of berries. For lunch and dinner, aim to fill your plate with a variety of colorful vegetables, lean proteins like fish or legumes, and whole grains such as quinoa or brown rice.
Another essential step is to embrace cooking at home, which allows you to control the ingredients and ensure they align with the Mediterranean Diet principles. Experiment with recipes that use olive oil as the primary fat source, and don’t be afraid to add herbs and spices to elevate the flavors. As you become more comfortable with these changes, you can gradually incorporate Mediterranean-inspired snacks, such as hummus with veggie sticks or a handful of nuts.
To support your newfound dietary habits, leverage the myriad of resources available. Books and online articles offer a wealth of information and recipe ideas. Joining support groups, whether in-person or online, can provide motivation and a sense of community. Furthermore, various apps and websites are designed to track your progress, suggest meal plans, and offer personalized tips.
Empowered with these strategies and resources, you can confidently embark on adopting the Mediterranean Diet, paving the way for improved health and well-being.